Lung Transplant
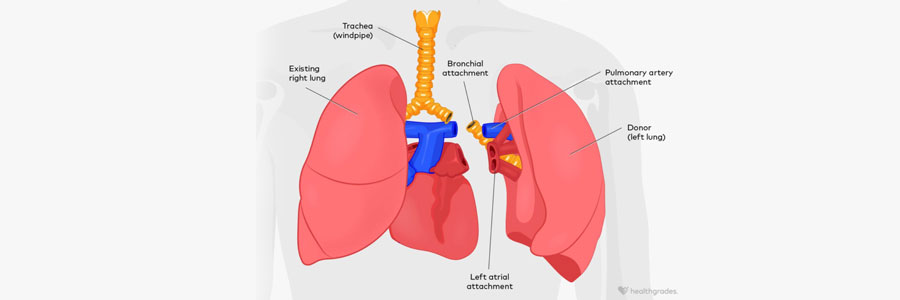
A lung transplant is a surgical procedure in which one or both diseased lungs are replaced with healthy lungs from a deceased donor. This life-saving operation is primarily for patients with severe lung diseases that have progressed to end-stage failure, where other treatments are no longer effective. The goal is to improve lung function, extend lifespan, and enhance quality of life.
Purpose of a Lung Transplant
The main purpose of a lung transplant is to provide a new set of functioning lungs for patients with severe, irreversible lung disease, allowing them to breathe more easily and improve their physical capabilities. Best Heart & Lung Transplant Surgeon In Palanpur Gujarat
Conditions That May Require a Lung Transplant
Some of the most common conditions that lead to a lung transplant include:
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Severe, progressive lung damage often due to smoking or environmental exposure.
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF): Scarring and stiffening of lung tissue without a known cause, leading to severe breathing difficulties.
- Cystic Fibrosis (CF): A genetic disorder that causes thick mucus buildup, leading to severe lung damage over time.
- Pulmonary Hypertension: High blood pressure in the lungs' blood vessels, which strains the heart and impedes lung function.
- Sarcoidosis: An inflammatory disease that can cause lung damage in some patients, leading to advanced fibrosis.
- Other Progressive Lung Diseases: Conditions such as interstitial lung disease and bronchiectasis that may lead to end-stage lung failure.
Types of Lung Transplants
- Single Lung Transplant: Only one diseased lung is replaced. Often done for conditions that affect only one lung or for patients who may not be able to tolerate a more extensive surgery.
- Double Lung Transplant: Both lungs are replaced. This is common for patients with diseases affecting both lungs, like cystic fibrosis.
- Heart-Lung Transplant: In rare cases, both the heart and lungs are transplanted together. This is done when both organs are severely affected, often due to pulmonary hypertension or congenital heart defects.
Benefits of a Lung Transplant
- Extended Life Expectancy: A successful lung transplant can add years to a patient’s life, especially for those with diseases that have no other effective treatment options.
- Improved Quality of Life: Many recipients experience significant improvement in breathing ability, physical activity, and overall well-being.
- Symptom Relief: Severe symptoms like breathlessness, chronic cough, and fatigue can be greatly reduced after a lung transplant.
- Increased Independence: Patients may regain the ability to engage in daily activities and exercise without severe limitations.
