ECMO & Mechanical Circulatory Support
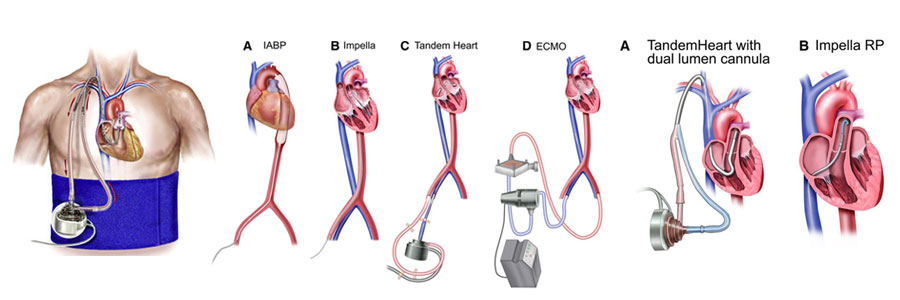
ECMO (Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation) and Mechanical Circulatory Support (MCS) are advanced life-support systems used to assist or replace the function of the heart and lungs in patients with severe cardiac or respiratory failure. These interventions are crucial for critically ill patients whose organs are too compromised to function effectively on their own.
ECMO (Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation)
Purpose: ECMO provides temporary support for patients with severe respiratory or cardiac failure, allowing the heart and lungs to rest and recover. It oxygenates the blood outside the body (extracorporeally) and removes carbon dioxide, essentially acting as an artificial lung and/or heart.
Types of ECMO:
- VV-ECMO (Veno-Venous ECMO): Primarily supports lung function. Blood is drawn and returned through veins, and oxygenation occurs outside the body. This is used in cases of severe respiratory failure where the heart function is normal.
- VA-ECMO (Veno-Arterial ECMO): Supports both heart and lung function. Blood is drawn from a vein, oxygenated, and returned to an artery, providing oxygenated blood directly to the arterial system. This is used for severe cardiac and/or respiratory failure.
Common Uses:
- Severe respiratory failure (e.g., ARDS, pneumonia, COVID-19 complications).
- Cardiac arrest or severe heart failure.
- Bridge to lung or heart transplant.
- Postoperative support in high-risk heart surgery.
Mechanical Circulatory Support (MCS)
Purpose: MCS devices are used to support or replace heart function, helping to circulate blood effectively in patients with advanced heart failure or shock. Unlike ECMO, which supports both respiratory and cardiac functions, MCS is focused solely on assisting or replacing the pumping function of the heart.
Types of Mechanical Circulatory Support:
- Ventricular Assist Devices (VADs): VADs are implanted devices that help the heart pump blood. They can support the left ventricle (LVAD), right ventricle (RVAD), or both (BiVAD).
- Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump (IABP): A balloon is placed in the aorta and inflates and deflates in sync with the heart's cycle, aiding blood flow and reducing the workload on the heart. It is commonly used in acute cases of heart failure or post-cardiac surgery.
- Impella Device: A catheter-based device that assists the heart by pulling blood from the left ventricle and expelling it into the aorta, thereby supporting blood flow and decreasing heart workload. It is often used for high-risk cardiac procedures or acute cardiogenic shock.
- Total Artificial Heart (TAH): In extreme cases, where both ventricles are failing, the TAH can completely replace the function of the heart. It is used as a bridge to transplant or as a destination therapy.
Common Uses:
- Cardiogenic shock (a condition where the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs).
- Advanced heart failure.
- Post-cardiac surgery complications.
- Bridge to heart transplantation.
